Available on https://psyarxiv.com/etk7g/, this is a comment on a recent article in the New England Journal of Medicine (Coomarasamy et al., 2019). A response by the authors will follow at a later point.
A recent trial assessed the effectiveness of progesterone in preventing miscarriages.1 The number of live births was 74.7% (1513/2025) in the progesterone group and 72.5% (1459/2013) in the placebo group (p=.08). The authors concluded: “The incidence of adverse events did not differ significantly between the groups.”
This conclusion leaves unaddressed the degree to which the data undercut or support the progesterone hypothesis. To quantify such evidence we conducted Bayesian logistic regression.2,3 Under the no-effect model H0, the log odds ratio equals ψ=0, whereas under the positive-effect model H+, ψ is assigned a positive-only normal prior N+(μ,σ). A default analysis (i.e., μ=0, σ=1) reveals only weak evidence for H0.4 Figure 1 shows the evidence is weak for all combinations of μ in [0,0.30] and σ in [0.25,1]. R code for reproducing the analyses is available from https://osf.io/tu4sv/.
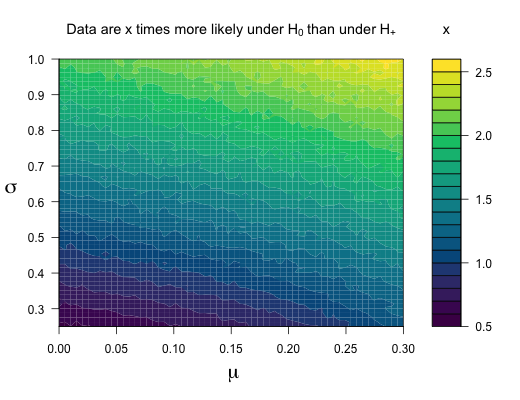
Figure 1. Across different priors, the evidence for no-effect H0 over positive-effect H+ is weak.
In sum, these data neither undercut nor support the progesterone hypothesis in compelling fashion.
References
- Coomarasamy A, Devall AJ, Cheed V, et al.. A randomized trial of progesterone in women with bleeding in early pregnancy. New England Journal of Medicine 2019;380:1815-24.
-
Kass RE, Vaidyanathan SK. Approximate Bayes factors and orthogonal parameters, with application to testing equality of two binomial proportions. Journal of the Royal Statistical Society: Series B (Methodological) 1992;54:129-44.
-
Gronau QF, Raj K. N. A., Wagenmakers EJ. (2019). Informed Bayesian inference for the A/B test. Manuscript submitted for publication and available on arXiv: http://arxiv.org/abs/1905.02068
-
Jeffreys, H. Theory of Probability. 1st ed. Oxford University Press, Oxford, UK, 1939.
About The Author

Quentin Gronau
Quentin is a PhD candidate at the Psychological Methods Group of the University of Amsterdam.

Eric-Jan Wagenmakers
Eric-Jan (EJ) Wagenmakers is professor at the Psychological Methods Group at the University of Amsterdam.